Vegan Diet for Heart Disease: A Comprehensive Guide
- Key Takeaways
- Prevalence of Heart Disease
- Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet for Heart Health
- Vegan Nutritional Components for Heart Health
- 5 Tips for Following a Heart-Healthy Vegan Diet
- Importance of Regular Exercise and Lifestyle Factors
- Plant-Based Diet Myths and Misconceptions
- Consulting with a Healthcare Professional
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Heart disease is a common problem affecting many Americans today. Did you know that it is the leading cause of death in the United States?
Discover how a plant-based lifestyle can help reduce your risk of heart disease and improve your overall well-being.
Ready to take control of your heart health? Let's explore the benefits of a vegan diet together!
Key Takeaways
- Heart disease is a major problem in the United States and a leading cause of death.
- Adopting a vegan diet can help reduce the risk of heart disease by reducing artery-clogging plaque, lowering cholesterol levels, improving blood flow and lowering blood pressure.
- A plant-based diet can also decrease the risk of obesity, improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, promote a healthier body weight, lower the risk of metabolic syndrome and reduce oxidative stress.
- Vegan nutritional components such as plant sterols, fiber and monounsaturated fats are important for heart health.
Prevalence of Heart Disease
Heart disease is a big problem in the U.S. Many people have this health issue. It is one of the top causes of death among Americans. Heart problems are linked with food habits, weight and lifestyle choices.
It's part of a growing number of diseases tied to what we eat, like diabetes and obesity. Diet changes can help fight this epidemic.
Traditional Treatments
Doctors often use drugs and surgery to treat heart disease. Drugs help the heart work better, break up blood clots, or lower cholesterol levels. Surgery can fix parts of the heart that don't work right.
But these treatments can't cure the disease. A healthy lifestyle is also important in managing heart disease. It involves eating healthy food, getting regular exercise, not smoking, and staying at a good body weight.
Lowering stress and controlling conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes also helps to keep your heart sound.
Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet for Heart Health
A plant-based diet offers numerous benefits for heart health. From reducing artery-clogging plaque to improving blood flow and lowering blood pressure, adopting a vegan lifestyle can significantly decrease the risk of heart disease.
Read on to learn more about the powerful effects of a plant-based diet on cardiovascular health.

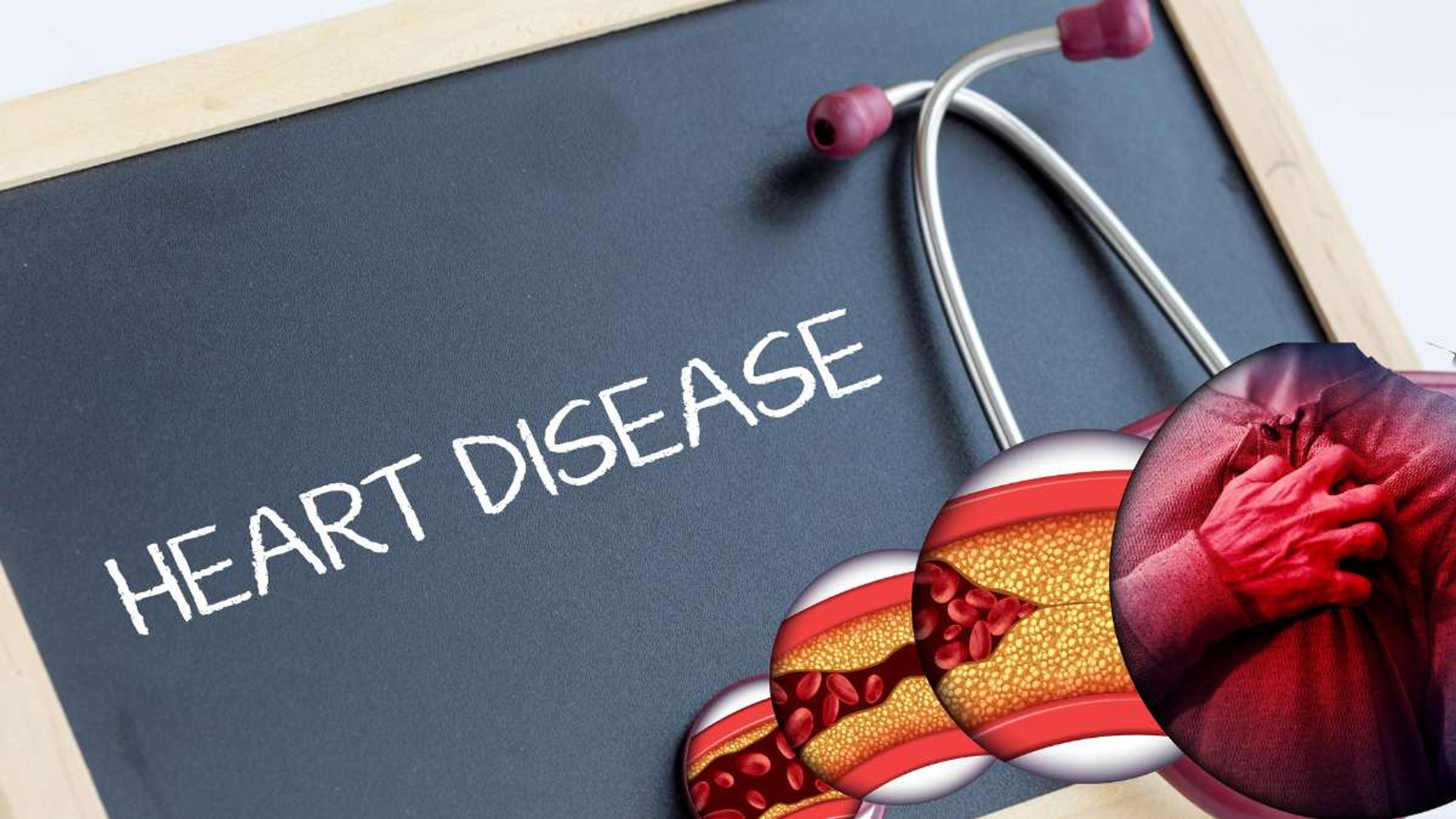
1. Reduction in artery-clogging plaque
Plaque is a sticky substance made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances that can narrow and harden the arteries over time.
Research has shown that adopting a plant-based diet can slow down this process and even reverse it in some cases. Avoiding animal products like meat and dairy that are high in saturated fats and cholesterol will lower our risk of developing atherosclerosis (the medical term for artery-clogging plaque) and protect our heart health.
2. Reduced cholesterol levels
Research suggests that adopting a vegetarian or vegan diets have shown to be effective in lowering total cholesterol, LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, as well as all-cause and cardiovascular mortality rates, compared to diets that include animal products.
This reduction in cholesterol is important because high cholesterol is a major risk factor for heart attacks and strokes. In fact, even people who start eating plant-based later in life can still experience these benefits. So by choosing a plant-based diet, you can take steps to improve your heart health by reducing your cholesterol levels.
3. Improved blood flow & Lower blood pressure
Studies have found that individuals following a plant-based diet had significantly lower blood pressure compared to non-vegans as vegan diets have been reported to decrease both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. This could potentially be due to the high potassium content in plant-based foods, which helps relax the walls of the blood vessels and improve circulation.
Therefore, adopting a vegan diet can be beneficial for maintaining healthy blood flow and reducing the risk of high blood pressure-related complications.
4. Decreased risk of obesity
Adherence to a healthful plant-based diet and consuming unprocessed plant foods in higher quantities can reduce the risk of obesity, low-grade inflammation, and impaired insulin sensitivity - all of which are often associated with an increased risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions.
Studies have shown that plant-based dietary patterns are linked to lower body weight and a decreased likelihood of developing obesity-related illnesses. By choosing a vegan diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts/seeds instead of high-fat animal products or processed foods, individuals can promote healthy weight management and reduce their risk of developing obesity.
5. Improved insulin sensitivity
Studies show that vegans, who follow a plant-based diet, have been found to improve insulin sensitivity, which is the body's ability to effectively use insulin to lower blood sugar levels and lower cholesterol production compared to non-vegans.
This means that their bodies are better able to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing conditions like diabetes. In fact, participants on a plant-based diet have experienced improvements in insulin sensitivity in just a matter of weeks, leading to weight loss and decreased HbA1c levels.
6. Anti-inflammatory effects
A plant-based vegan diet has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. This means that it can help reduce inflammation in the body, which is important for heart health. Inflammation is linked to various chronic diseases, including heart disease.
By reducing inflammation, a vegan diet may help protect against heart disease and improve cardiovascular health. Studies have also found that a plant-centered diet can lower markers of inflammation in the body over time, further supporting its benefits for heart health.
So, by choosing a plant-based vegan diet, you can potentially reduce inflammation and promote a healthier heart.
7. Healthier body weight
Plant-based diets have been found to help achieve a healthier body weight. Research has shown that individuals who follow plant-based diets tend to have lower body mass index (BMI) and are more likely to maintain a healthy weight compared to those following other eating patterns.
This is important because excess body weight is a risk factor for heart disease. By adopting a plant-based diet, you can not only improve your heart health but also support your efforts in achieving and maintaining a healthier body weight.
8. Lower risk of metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. These conditions include high blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, excess belly fat, and abnormal cholesterol levels. By adopting a plant-based diet, which is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes while avoiding animal products like meat and dairy, individuals can improve their insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation in the body.
This leads to a decreased risk of developing metabolic syndrome and its associated health complications. Research has shown that following a plant-based diet reduces the risk of death from cardiovascular disease by 40% and lowers the risk of heart disease death by 40%.
9. Reduced oxidative stress
A plant-based diet, such as a vegan or low-fat vegetarian diet, can help to reduce oxidative stress in the body. Oxidative stress is a condition where there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body.
It can lead to damage of cells and tissues, including those in the heart. By following a plant-based diet, which is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, individuals can increase their intake of antioxidants that help to neutralize free radicals.
This can have beneficial effects on heart health by reducing inflammation and improving overall cardiovascular function. So incorporating more plant-based foods into your diet could be helpful in reducing oxidative stress.
10. Enhanced cardiovascular function
A vegan diet can enhance cardiovascular function, which means it helps improve the way your heart and blood vessels work. Studies have shown that following a plant-based diet is associated with better cardiovascular health as it can lower blood pressure, improve blood flow, and reduce the risk of heart disease.
These foods provide essential nutrients and antioxidants that support heart health. Additionally, a vegan diet is typically low in saturated fats and cholesterol, which can contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries.
Vegan Nutritional Components for Heart Health
Important Nutrients to Consider
Plant sterols, fiber, and monounsaturated fats are important components of a heart-healthy vegan diet.
- Plant sterols, which are found in plant-based foods such as nuts, seeds, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, lower cholesterol levels.
- Fiber, also abundant in plant foods, can also contribute to lower cholesterol levels, regulate blood sugar levels, and maintain a healthy weight.
- Monounsaturated fats, such as those found in avocados and olive oil, have been linked to lower LDL cholesterol levels.
By including these nutrients in your diet, you can support heart health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
10 best Vegan foods for heart health
Plant-based diets are beneficial for heart health as they do not contain dietary cholesterol and are rich in fiber. Here are the top 10 vegan foods that promote a healthy heart:

- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support heart health.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are high in antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of heart disease.
- Whole grains: Oats, quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread provide fiber that helps manage cholesterol levels and maintain a healthy weight.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas are excellent sources of protein and fiber while being low in saturated fat.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are rich in heart-healthy fats like omega-3 fatty acids.
- Avocado: This creamy fruit is high in monounsaturated fats that can help lower bad cholesterol levels.
- Tomatoes: Packed with lycopene, tomatoes have been linked to reduced risk of heart disease.
- Garlic: This flavorful herb has been shown to improve blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Dark chocolate: In moderation, dark chocolate (70% cocoa or higher) can provide antioxidant benefits for heart health.
- Green tea: Known for its high antioxidant content, green tea has been associated with a decreased risk of heart disease.
5 Tips for Following a Heart-Healthy Vegan Diet
Include a variety of plant-based foods, focusing on whole foods for optimal heart health. Monitor your intake of saturated fats and sodium, consider supplements for essential nutrients, stay hydrated and active, seek professional guidance, and educate yourself on plant-based nutrition.

1. Include a Variety of Plant-Based Whole foods
To follow a heart-healthy vegan diet, it's important to include a wide variety of plant-based foods, especially whole foods. Whole foods are minimally processed and retain their natural nutrients.
Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds should be the foundation of your vegan diet. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants ensure that you're getting all the necessary nutrients for optimal heart health and overall well-being.
To successfully follow a heart-healthy vegan diet, it's important to educate yourself on plant-based nutrition. This means understanding the different nutrients found in plant foods and how to obtain them in adequate amounts.
2. Monitor Saturated Fats and Sodium Intake
To maintain a heart-healthy vegan diet, it is important to monitor the intake of saturated fats and sodium. Saturated fats can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease, so it's crucial to limit foods like coconut oil, palm oil, and processed snacks.
Reading nutrition labels and choosing foods with less sodium is also key. Too much sodium can contribute to high blood pressure, which is a risk factor for heart disease. By being mindful of these factors, individuals can support their cardiovascular health while following a plant-based lifestyle.
3. Consider Supplements for Essential Nutrients
Vegans may have lower levels of EPA, DHA, selenium, and zinc, compared to those who consume animal products, unplanned vegan diets can sometimes be lacking in certain essential nutrients. To address these potential gaps in nutrition, it is important for vegans to consider consuming more plant-foods rich in these nutrients, failing which, take supplements.
One essential supplement that vegans should consider taking is vitamin B12. It is primarily found in animal-based foods such as meat and dairy products. Since vegans avoid these sources, they are at a higher risk of deficiency. Taking a vitamin B12 supplement ensures an adequate intake of this crucial nutrient for energy production and nerve function.
Omega-3 fatty acids are another important nutrient that may need supplementation on a vegan diet. While plant sources like flaxseed provide an omega-3 called ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), the body needs to convert it into EPA and DHA for optimal heart health and brain function.
This conversion process can be inefficient in some individuals. Therefore, considering an algae-based omega-3 supplement can help meet the body's requirements for these beneficial fats.
4. Staying Hydrated and Active
Staying hydrated and staying active are important for maintaining a healthy heart.
Drinking enough water helps to keep our blood flowing smoothly and can lower the risk of fatal heart disease. It is recommended to drink at least 8 cups of water per day.
Being physically active also has many benefits for our hearts, such as improving blood flow and reducing the risk of cardiovascular conditions like heart attack and stroke. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise each week. Remember to choose activities that you enjoy, such as walking, swimming, or dancing, to make it easier to stay active regularly.
5. Seeking Professional Guidance
If you have heart disease and want to follow a vegan diet, seeking professional guidance is important. Professionals, like registered dietitians or plant-based doctors, can give you tips on how to follow a heart-healthy vegan diet.
They can help you understand the benefits of this diet and any potential drawbacks. They will also make sure that you get all the nutrients your body needs while following a vegan lifestyle.
Seeking professional guidance is crucial for individuals with heart disease who want to adopt a plant-based diet successfully.
Importance of Regular Exercise and Lifestyle Factors
Regular exercise and lifestyle factors play a crucial role in maintaining heart health. Discover how staying active, managing stress, and getting enough sleep can contribute to a healthy heart.

1. Exercise for heart health
Regular exercise is vital for maintaining a healthy heart. It can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by improving various risk factors. Exercise promotes weight loss and helps to maintain a healthy weight, which is important for heart health.
It also improves insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, reducing the risk of diabetes. Regular physical activity can lower blood pressure and improve lipid profiles, reducing the risk of hypertension and dyslipidemia.
Additionally, exercise helps improve endothelial function, which reduces the risk of atherosclerosis. So make sure you incorporate regular exercise into your routine to keep your heart healthy!
2. Stress management
Managing stress is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart. Stress can contribute to inflammation and increase the risk of heart disease. To effectively manage stress, it is important to engage in activities that promote relaxation, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga.
Making time for hobbies and activities that bring joy and reduce stress levels can also be beneficial. Additionally, seeking support from loved ones or joining support groups can provide an outlet for sharing feelings and reducing emotional burden.
Taking breaks when needed and prioritizing self-care are essential steps towards managing stress and improving overall heart health.
3. Adequate sleep
Getting enough sleep is crucial for maintaining a healthy vegan diet and preventing heart disease. Short sleep duration and poor sleep quality can negatively impact our dietary habits.
It's important to prioritize adequate sleep as it is associated with regular exercise and other lifestyle factors that are essential for heart health. Factors such as nutrition, stimulants, and physical activity can affect the quality of our sleep.
In fact, research suggests that a vegetarian diet may improve sleep quality by positively influencing mental health, particularly depression. Sleep and nutrition are interconnected, so maintaining a healthy diet can positively influence the quality of our sleep.
Plant-Based Diet Myths and Misconceptions
Many people believe that a plant-based diet lacks protein, causes nutrient deficiencies, and offers bland and boring food options. However, these are just misconceptions as a well-planned vegan diet can provide all the necessary nutrients and offer a variety of delicious meals.
Additionally, with the increasing popularity of plant-based eating, there are now numerous options for dining out while following a vegan diet.

Lack of protein
Plant-based diets have often been criticized for their perceived lack of protein. However, this concern is largely unfounded. Plant-based diets can provide sufficient amounts of protein through a variety of sources such as legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds.
Protein deficiency is not a concern for those who eat less meat since protein is found in all foods. It's important to note that not all plant-based foods are healthy, as some vegan processed foods can be high in sugar, salt, and saturated fats.
By including a variety of plant-based protein sources in your diet, you can easily meet your daily protein needs while reaping the many health benefits associated with a plant-based lifestyle.
Nutrient deficiencies
It is a common misconception that a plant-based diet can lead to nutrient deficiencies. However, with proper planning and attention to food choices, it is entirely possible to meet all the necessary nutrient requirements for heart health on a vegan diet.
Plant-based diets can provide an abundance of essential nutrients like protein, iron, calcium, and essential fatty acids. Foods such as beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, seeds, whole grains, leafy greens, and fortified plant milks are excellent sources of these nutrients.
By including a variety of these foods in your meals and snacks throughout the day, you can ensure that your body receives all the nourishment it needs while supporting heart health.
Bland and boring food
Contrary to a common misconception, plant-based diets are not associated with bland and boring food. In fact, vegan cuisine offers a wide variety of flavorful and satisfying options beyond just salads or "rabbit food." With the abundance of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds available in a plant-based diet, there are countless possibilities for creating delicious meals that are both good for your heart health and enjoyable to eat.
By focusing on nutrient-dense whole foods and exploring different cooking techniques and flavors from various cuisines around the world, you can easily make your heart-healthy vegan meals exciting and tasty.
Difficulty eating out
Eating out can be a challenge when following a vegan diet for heart health. Many restaurants and fast food chains may not have extensive vegan options on their menus, making it difficult to find suitable meals.
However, there are ways to navigate this challenge. Some tips include researching restaurants in advance that offer vegan options or can accommodate dietary restrictions, communicating with the restaurant staff about your dietary needs, and being flexible by customizing menu items to make them plant-based.
It's also helpful to plan ahead and carry snacks or choose establishments that prioritize healthy, whole-food options. By being proactive and prepared, you can still enjoy dining out while adhering to your heart-healthy vegan diet.
Consulting with a Healthcare Professional
Working with a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance and ensure you are meeting your nutritional needs on a vegan diet. To learn more about the importance of professional assistance and other key factors for heart health, continue reading.

Working with a registered dietitian
If you have heart disease and are following or considering a vegan diet, it may be helpful to work with a registered dietitian. Registered dietitians can assess your dietary needs, provide personalized nutritional counseling, and create meal plans tailored to your specific health condition.
They can ensure that you are getting all the essential nutrients from your plant-based diet while managing your heart disease effectively. By collaborating with a registered dietitian associated with a healthcare professional, you can receive expert guidance and support on how to best optimize your heart health through a vegan lifestyle.
Monitoring your health
It is important to monitor your health when following a vegan diet for heart disease. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals, including registered dietitians, can help ensure that you are meeting your nutritional needs and addressing any potential deficiencies.
Monitoring key health markers such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels can provide insights into the effectiveness of the vegan diet in managing heart disease risk factors.
Additionally, staying informed about plant-based nutrition and seeking professional guidance can help optimize your heart health journey.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a vegan diet can be a powerful tool in preventing and managing heart disease. By focusing on plant-based foods and minimizing the intake of animal products, individuals can reduce plaque buildup in arteries, lower cholesterol levels, improve blood flow, and decrease the risk of obesity.
Incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich plant foods along with regular exercise and lifestyle factors is key to maintaining heart health. Consider consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance on adopting a heart-healthy vegan diet.
FAQs
1. What is a vegan diet for heart disease?
A vegan diet for heart disease is a type of plant-based diet with no red meat that may help prevent and even reverse coronary artery disease according to the American Heart Association.
2. Can a vegan diet help prevent heart disease?
Yes, a vegan diet can help prevent heart disease. Vegan diets are typically low in saturated fat and cholesterol, which are risk factors for heart disease. They are also rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and plant-based proteins, which have been shown to promote cardiovascular health.
3. Can going vegetarian provide the same benefits as a vegan diet against coronary heart diseases?
Vegetarianism too can lower risk for coronary heart diseases like meta-analysis studies show but complete removal of animal products as in Veganism might be more beneficial towards public health.
4. Who should I talk to before switching to the vegan diet?
Talk with your healthcare provider about transitioning into types of plant-based diets including Veganism as it's a significant change especially if you're dealing with cardiology related issues or have stents from previous operations.
5. Are there any popular figures promoting this kind of dietary approach aimed at better cardiac health?
Yes! Dean Ornish who works closely with Cleveland Clinic and American College Of Cardiology suggests moving towards vegetarianism or Veganism could support managing coronary diseases.

