What Can Vegetarians Eat For a Balanced Plant-Based Diet?

- Key Takeaways
- What Can Vegetarians Eat on a Plant-Based Diet?
- Essential Nutrients for Vegetarians
- Health Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
- Planning a Healthy Plant-Based Diet
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Navigating a healthy plant-based diet can seem daunting to a vegetarian in the making. With an array of nutritious, affordable, and delicious foods - from fruits and vegetables to whole grains and legumes - there's no shortage of options.
This comprehensive guide will shed light on what vegetarians can eat, tackling aspects such as essential nutrients required for optimal health, benefits inherent in a vegetarian diet, and how to plan meals effectively.
Ready to savor the bounty of Mother Nature's pantry?
Key Takeaways
- Vegetarians can enjoy a wide variety of foods on a plant-based diet, including whole fruits and vegetables, legumes and beans, grains and cereals, nuts and seeds, plant-based proteins, dairy or dairy alternatives (for lacto-vegetarians), and plant-based fats and oils.
- Essential nutrients for vegetarians include protein sources such as legumes, tofu, tempeh, nuts, seeds, and whole grains; calcium and vitamin D from fortified plant-based products; iron from leafy greens, lentils, and fortified cereals; omega-3 fatty acids from chia seeds and Brussels sprouts; and vitamin B12 from eggs or dairy products (for vegetarians) or fortified plant-based milk or cereals (especially for vegans).
- Health benefits of a plant-based diet include reduced risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, high blood pressure and diabetes. Vegetarian diets also support weight management due to their high fiber content.
- Fortified foods contain added vitamins & minerals that aren't naturally present in them and are meant to improve people's levels of particular nutrients. Cereal is one of the most commonly fortified foods.
What Can Vegetarians Eat on a Plant-Based Diet?
Vegetarians on a plant-based diet can enjoy a wide variety of foods, including whole fruits and vegetables, legumes and beans, grains and cereals, nuts and seeds, plant-based proteins like tofu or tempeh, dairy or dairy alternatives (for lacto-vegetarians), and plant-based fats and oils.
Whole fruits and vegetables

Whole fruits and vegetables are the foundation of a nutritious vegetarian diet. Rich in necessary vitamins, minerals, and fiber, these vegetarian sources can be enjoyed in various forms — from crisp salads to warming soups or even as smoothies.
Apples, bananas, grapes, strawberries and citrus fruits like oranges and lemons are excellent choices for fruit lovers. For those who favor vegetables, there's an array of options including peppers for a crisp bite or leafy greens such as kale for nutrient-density.
Cruciferous veggies like broccoli offer both texture and substantial health benefits while adding variety to your plate. The possibilities with whole fruits and vegetables are infinite; they can be incorporated into all meals seamlessly ensuring your plant-based diet is fully flavored while covering all nutritional needs efficiently.
Legumes and beans

Legumes and beans are powerful plant-based foods that should hold a prominent place in any vegetarian's diet. They are not just great sources of protein, but also rich in nutrients like fiber, iron, and folate.
Foods such as lentils, chickpeas, peas, soy products like tofu and tempeh are all part of this nutritious category.
From simmered black beans added to burritos to crunchy roasted chickpeas for snacking or a hearty lentil soup - the culinary possibilities are endless. Plus, incorporating these plant-based proteins into meals can have amazing health benefits too.
For instance, regularly eating legumes has been linked with lower blood pressure and reduced risk of heart disease – an ideal source of protein & a great habit for those pursuing healthy eating habits on a vegetarian diet.
A variety-packed meal plan might see you adding chickpeas to salads one day while enjoying edamame stir-fry the next followed by a comforting bowl of lentil curry or even some toasted almond butter spread generously on whole grain toast in between meals—proof that meeting nutritional needs through variety is key to maintaining balanced nutrition on a plant-based diet.
Grains and cereals

Grains and cereals form an essential part of a healthy plant-based diet. Foods like quinoa, brown rice, whole wheat bread, oats, and barley not only offer rich sources of fiber but also good sources that provide necessary nutrients such as iron and B vitamins.
From scrumptious breakfast oatmeal to enticing dinner entrees with quinoa or brown rice, these foods are versatile in any vegetarian meal plan. Incorporated properly into your meals, they can help meet your daily nutritional needs - all while skilfully spicing up your vegetarian food repertoire.
Nuts and seeds
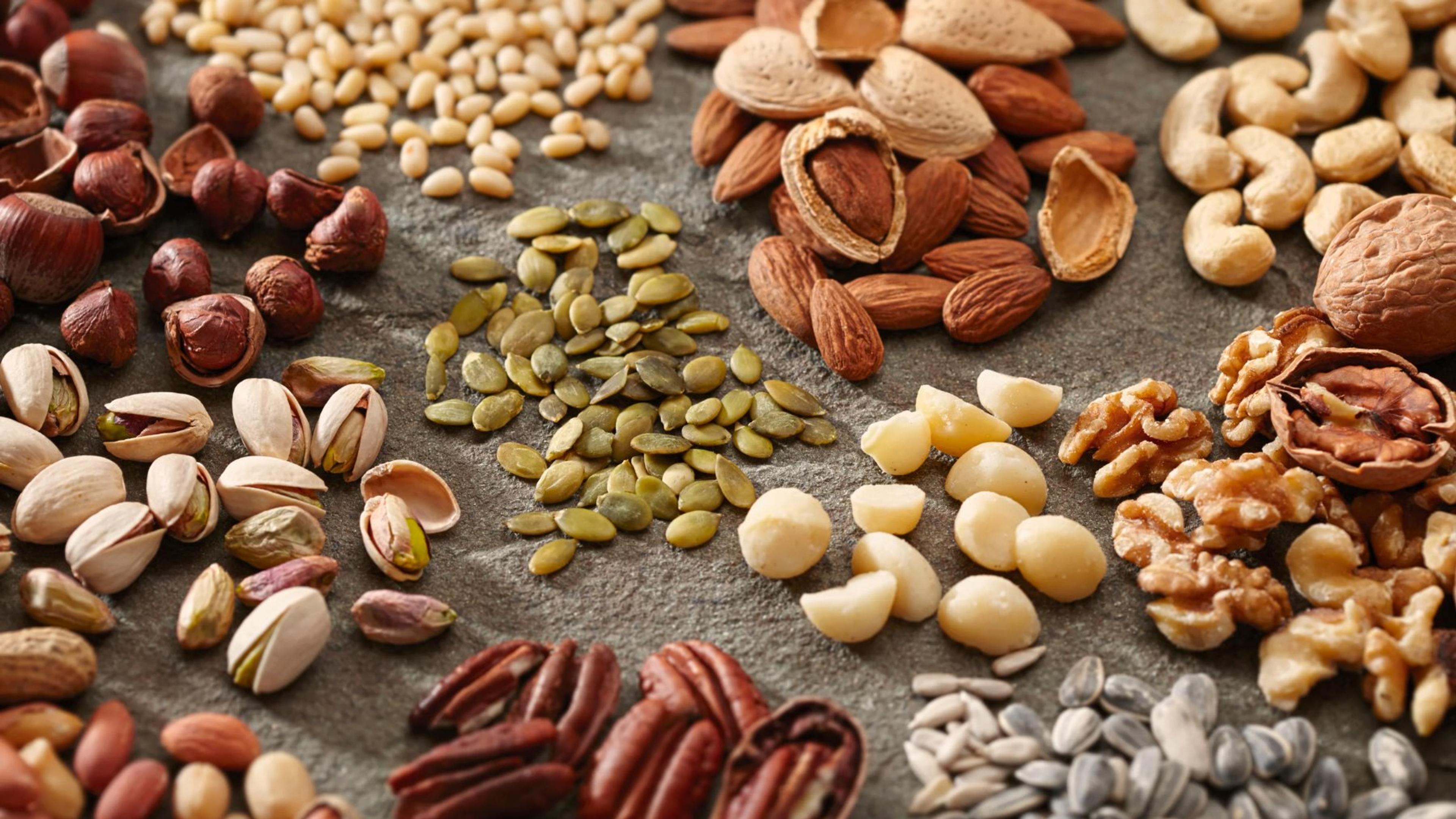

Nuts and seeds are an essential part of a healthy plant-based diet for vegetarians and vegans. These little powerhouses of nutrition not only add flavor and texture to meals but also provide a wide range of health benefits.
Packed with protein, healthy fats, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, nuts and seeds are linked to positive outcomes like improved heart health and weight management. Almonds, cashews, macadamia nuts, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds are just a few examples of these nutrient-rich options that can easily be incorporated into your favorite dishes or enjoyed as a snack on their own.
So go ahead and sprinkle some chopped almonds on your morning oatmeal or toss some pumpkin seeds into your salad for that extra crunch – your taste buds will thank you while reaping the nutritional rewards!
Plant-based proteins

Plant-based proteins are a crucial component of a healthy vegetarian diet. Contrary to popular belief, there are plenty of plant sources that provide all the essential amino acids needed for optimal health and muscle function.
Foods such as lentils, chickpeas, tofu, tempeh, quinoa, and soy products like edamame and soy milk are excellent sources of protein for vegetarians. These plant-based proteins not only provide the body with necessary building blocks but also offer other benefits such as fiber and phytonutrients which can contribute to overall health.
Incorporating a variety of plant-based proteins into your meals ensures that you meet your protein needs while enjoying delicious vegetarian dishes.
Dairy and Eggs (if Vegetarian) or Dairy alternatives (if Vegan)

Vegetarians have a few options when it comes to including dairy and eggs in their plant-based diet. For those who are ovo-vegetarian, which means they include eggs in their diet, incorporating dairy and eggs is straightforward.
They can enjoy foods like milk, cheese, yogurt, and butter made from animal sources alongside their plant-based meals. On the other hand, vegans choose not to consume any animal products, including dairy and eggs.
However, there are plenty of delicious alternatives available that can easily replace these ingredients. Dairy alternatives such as oat milk, soymilk, coconut milk, and almond milk provide a creamy texture and taste similar to regular milk.
Plant-based fats and oils

Plant-based fats and oils are an essential part of a vegetarian diet, providing valuable nutrients and enhancing the flavor of dishes. Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and coconut oil are all excellent sources of healthy fats that can be used in cooking or as dressings for salads.
These plant-based fats provide important omega-3 fatty acids which support brain health and reduce inflammation in the body. By incorporating a variety of plant-based fats into your meals, you can ensure that your body receives the necessary nutrients while enjoying delicious flavors.
So go ahead and experiment with different oils and add some avocado slices to your next salad for a healthy boost!
Essential Nutrients for Vegetarians
Discover the key nutrients that vegetarians need to pay attention to for a healthy plant-based diet. Read on to find out more.
Protein sources
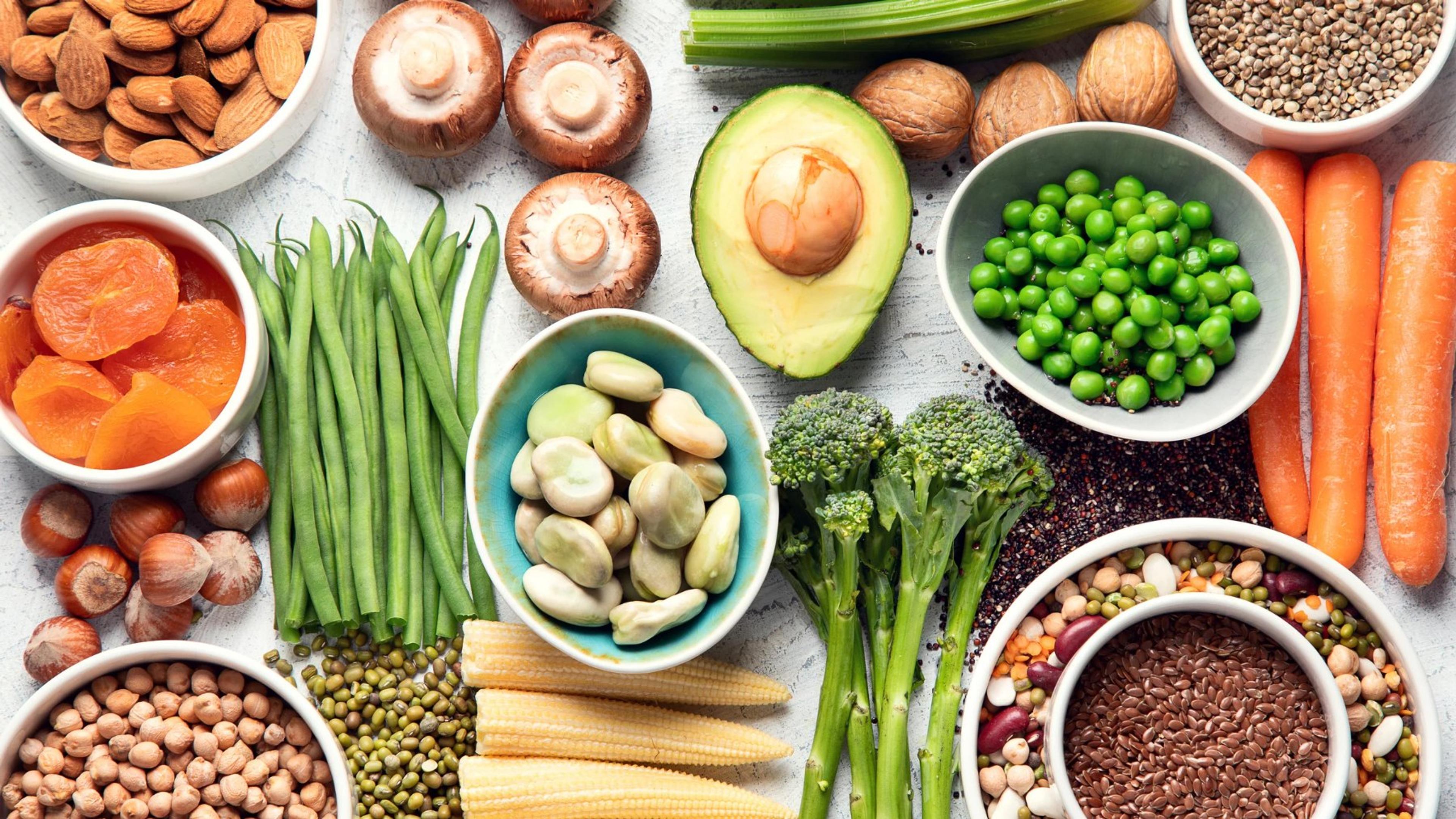

Protein is an essential component of a healthy diet, and as a vegetarian, it's important to ensure you're getting enough protein from plant-based sources. Fortunately, there are plenty of options available! Legumes like lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are excellent sources of protein and can be incorporated into a variety of dishes such as soups, stews, and salads.
Other protein-rich foods include tofu, tempeh, edamame (young soybeans), and seitan (made from gluten). Nuts and seeds like almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and hemp seeds also provide protein along with healthy fats.
Additionally, whole grains such as quinoa and brown rice contain notable amounts of protein. By including these diverse plant-based proteins in your meals and snacks throughout the day, you can easily meet your nutritional needs while enjoying delicious vegetarian cuisine.
Calcium and Vitamin D
Calcium and vitamin D are essential nutrients for maintaining good bone health, making them particularly important for vegetarians. While calcium is commonly associated with dairy products, there are plenty of plant-based options available as well. Some examples include low-fat or fat-free milk alternatives like soy or almond milk, fortified plant-based milk, yogurt, cheese alternatives made from nuts or soybeans and fortified ready-to-eat cereals.
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and can be obtained through sunlight exposure or by consuming foods that are enriched with vitamin D2, which is vegan-friendly. It's crucial for vegetarians to ensure they're getting enough calcium and vitamin D in their diet to maintain overall health and prevent deficiencies in these vital nutrients.
Iron

Iron is an essential nutrient for vegetarians, as it plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. While plant-based sources of iron may not be as easily absorbed by the body compared to iron from meat, there are ways to enhance absorption.
One effective method is consuming vitamin C-rich foods alongside iron-rich plant foods. Foods high in iron along with Vitamin C rich foods help maximize iron uptake and ensure vegetarians maintain healthy iron levels.
It's worth noting that while a vegan diet can still provide sufficient iron, absorption may be lower than from meat sources. To meet their iron needs, vegetarians should focus on consuming a diverse range of iron-rich plant foods such as leafy greens, lentils, and fortified cereals or consider talking to a dietitian about potential supplements if necessary.
Omega-3 fatty acids
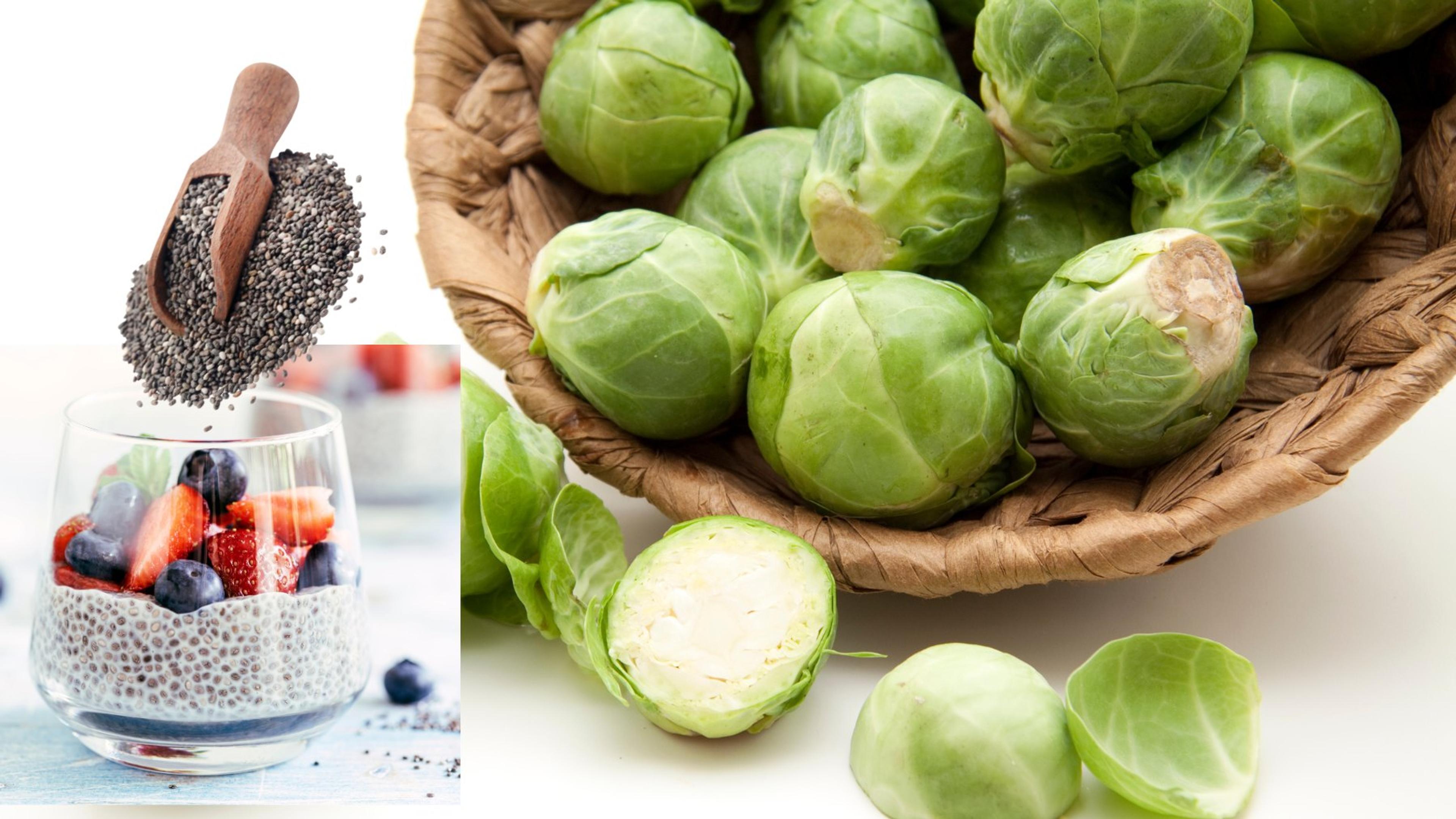

Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients for maintaining a healthy plant-based diet. These fats play a crucial role in supporting heart health, brain function, and reducing inflammation in the body.
While fish and seafood are commonly touted as rich sources of omega-3s, vegetarians can also obtain these beneficial fats from plant-based foods. Chia seeds, for example, are not only packed with fiber and protein but also provide a great source of omega-3 fatty acids.
Brussels sprouts are another excellent option for vegetarians looking to boost their intake of these essential fats. If needed, there are also vegetarian omega-3 supplements available that use algal oil as a sustainable alternative to fish oil capsules.
Vitamin B12

Vegetarians and vegans need to pay careful attention to their vitamin B12 intake, as this essential nutrient is primarily found in animal products. Vitamin B12 is crucial for maintaining healthy nerves, red blood cells, and DNA building.
While vegetarians who consume eggs and dairy products have more options for obtaining vitamin B12, such as through milk, cheese and fortified plant-based milk or cereals. Vegans have a more limited list of sources but can still obtain it from fortified plant-based milk, soy products and breakfast cereals.
It's important to be aware of potential deficiency symptoms and consider supplementation if necessary. Understanding the sources and potential deficiency risks of vitamin B12 is crucial for individuals following a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle.
Health Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
A plant-based diet offers numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of chronic diseases, weight management, improved digestion, enhanced nutrient intake, and increased energy levels.
Discover how you can achieve these benefits by adopting a healthy plant-based eating plan. Read more to start your journey towards better health today!
Reduced risk of chronic diseases
A plant-based diet offers a multitude of benefits, with one major advantage being a reduced risk of chronic diseases. Studies have shown that individuals who follow a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle are less likely to develop heart disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and certain types of cancer.
By focusing on whole fruits and vegetables, legumes and beans, grains and cereals, nuts and seeds, and plant-based proteins like tofu and chickpeas, you can nourish your body with essential nutrients while minimizing the intake of harmful saturated fats typically found in animal products.
Furthermore, a well-balanced plant-based diet can help maintain a healthy weight - an important factor in reducing the risk of cancer. So by embracing more plant-based foods in your cooking repertoire, you're not only taking care of your own health but also contributing to a healthier planet!
Weight management

Maintaining a healthy weight is a common concern for many individuals, and a plant-based diet can be an effective tool for achieving this goal. Plant-based diets are typically lower in calories and higher in fiber compared to diets that include meat and processed foods.
The increased fiber content helps promote feelings of fullness, which can lead to reduced calorie intake and support weight loss efforts. Additionally, plant-based diets tend to be rich in nutrient-dense whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
These foods provide essential vitamins and minerals while being naturally low in fat and high in water content. Studies have shown that individuals who follow a plant-based diet often have lower body mass indexes (BMI) than those who consume animal products regularly.
Improved digestion

Including more plant-based foods in your diet can lead to improved digestion. Plant-based foods are packed with fiber, which helps regulate bowel movements and promote a healthy digestive system.
Fiber adds bulk to the stool, preventing constipation and promoting regularity. Additionally, a plant-based diet can help alleviate symptoms of indigestion and acid reflux due to its high content of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties.
By incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds into your meals, you provide your body with essential nutrients that support gut health and overall digestion.
Enhanced nutrient intake

A plant-based diet can significantly enhance your nutrient intake, providing you with a wide range of essential vitamins and minerals. Fruits, vegetables, legumes, grains, nuts, and seeds are all powerhouses of nutrients that can boost your overall health.
These foods are packed with fiber to improve digestion and keep you feeling full for longer periods. They also contain high levels of vitamins A, C, E, K, and folate, as well as minerals like iron and calcium that are crucial for optimal health.
By embracing a plant-based diet, you're nourishing your body with an abundance of nutrients that promote vitality and well-being.
Increased energy levels

A plant-based diet can provide a significant boost to your energy levels. By incorporating nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes into your meals, you're fueling your body with the necessary vitamins and minerals for optimal performance.
These foods are rich in complex carbohydrates that release energy slowly throughout the day, preventing those mid-afternoon crashes. In addition to keeping you energized, plant-based diets are also often higher in fiber, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and prevents spikes and crashes in energy.
So if you're looking for an extra dose of vitality throughout the day, consider embracing a plant-based diet - it's not only beneficial for overall health but can also leave you feeling more invigorated than ever before.
Planning a Healthy Plant-Based Diet
To plan a healthy plant-based diet, it is important to consider meal planning, nutrient balance, variety, reading food labels, and cooking and preparing meals. Discover the secrets to maintaining a balanced vegetarian lifestyle here!
Meal planning

Meal planning is a crucial aspect of maintaining a healthy plant-based diet. By taking the time to plan your meals ahead, you can ensure that you are getting all the necessary nutrients and variety in your diet.
It also helps prevent last-minute unhealthy food choices and saves you time during busy weekdays. When meal planning, be sure to incorporate a mix of whole grains, legumes, vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds to provide a balanced intake of essential nutrients like protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
You can also experiment with different cuisines and recipes to keep things interesting and exciting. With proper meal planning, you'll be well-equipped to stick to your plant-based lifestyle while enjoying delicious and nutritious meals every day!
Ensuring nutrient balance

A key aspect of planning a healthy plant-based diet is ensuring nutrient balance. While vegetarian diets can provide all the necessary nutrients for optimal health, it's important to include a variety of different foods to meet your body's needs.
One way to do this is by incorporating a mix of fruits, vegetables, legumes, grains, nuts, and seeds into your meals.
These food groups offer a wide range of essential vitamins and minerals that are needed for overall health. For example, leafy greens like spinach and kale are excellent sources of calcium and iron.
Legumes such as chickpeas and lentils provide protein along with fiber. Whole grains like quinoa and brown rice offer complex carbohydrates for sustained energy.
By incorporating these diverse food sources into your diet on a regular basis, you can ensure that you're getting all the nutrients you need for optimal health as a vegetarian or vegan.
It's also helpful to consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional who specializes in plant-based nutrition to ensure proper nutrient balance and address any specific dietary concerns or goals you may have.
Incorporating variety

A key aspect of a healthy plant-based diet is incorporating a variety of foods. By including a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and legumes in your meals, you can ensure that you're getting all the essential nutrients your body needs.
Different plant-based foods offer unique combinations of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that contribute to overall health and well-being. For example, leafy greens like kale and spinach are excellent sources of calcium and iron, while nuts such as walnuts provide heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
Mixing up your ingredients not only keeps your taste buds happy but also ensures that you're nourishing yourself with a diverse array of nutrients. So go ahead and explore the colorful world of plant-based cuisine – there's an abundance of flavors waiting for you!
Reading food labels

Understanding food labels is essential for planning a healthy plant-based diet and knowing what vegetarians can eat. Food packaging can be confusing, but focusing on specific information on the food label can help determine what's in the food.
By looking at the nutritional content and ingredients listed, you can make informed choices about whether a product aligns with your dietary needs. This is particularly important for vegetarians who need to be aware of animal-derived ingredients like dairy or eggs that may be present in certain foods.
Reading food labels ensures that you are mindful of the nutrients, calories, and potential allergens in packaged products, allowing you to make informed decisions about what goes into your meals.
Cooking and preparing meals

Cooking and preparing meals is an essential aspect of maintaining a healthy plant-based diet. By taking control of your kitchen, you can ensure that you're incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into your meals.
Experiment with different cooking techniques, such as grilling, baking, steaming, or stir-frying, to enhance flavors and retain the nutritional value of your ingredients. Don't be afraid to get creative with spices and herbs to add depth and complexity to your dishes.
Planning ahead by meal prepping can also help save time and make it easier to stick to your dietary goals throughout the week. So put on your apron and get ready to explore the world of delicious vegetarian cuisine!
Conclusion
In conclusion, a vegetarian diet offers a wide variety of delicious and nutritious options for those looking to embrace a plant-based lifestyle. From colorful fruits and vegetables to protein-rich legumes and grains, there are countless possibilities that cater to different tastes and dietary preferences.
With careful planning and attention to essential nutrients, vegetarians can enjoy a healthy and balanced diet while reaping the many benefits it brings. So whether you're new to vegetarianism or simply looking for inspiration, explore the fantastic world of plant-based foods and discover the endless culinary possibilities they have to offer!
FAQs
1. What foods can vegetarians eat?
Vegetarians can eat a wide variety of plant-based foods including fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and plant-based protein sources like tofu and tempeh. They can also enjoy dairy products and eggs if they follow a lacto-ovo vegetarian diet.
2. How do vegetarians get enough protein in their diet?
Vegetarians can meet their protein needs by consuming a combination of different plant-based protein sources such as beans, lentils, quinoa, tofu, tempeh, seitan, edamame, chickpeas, and various types of nuts and seeds. It's important for vegetarians to make sure they include a variety of these protein-rich foods in their meals.
3. Can vegetarians still get all the necessary nutrients without meat?
Yes! With proper planning and attention to their food choices, vegetarians can obtain all the necessary nutrients from plant-based sources alone. By incorporating a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds and fortified plant-based milk alternatives into their diets. They will be able to meet their nutritional needs for vitamins (like B12), minerals (such as iron and calcium), healthy fats (found in avocados or olive oil), etc.
4. Are there any potential health benefits to adopting a vegetarian diet?
A well-balanced vegetarian diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes and plant-based proteins can offer numerous health benefits like reduced risk of heart disease, strokes, hypertension, colon cancer, etc. It may also help with weight management since it tends to be lower in saturated fat while being rich in fiber – which aids digestion & promotes feelings of fullness.

